定义
通过与波动器中的快速电子相互作用而发生光放大的激光设备。
自由电子激光器是一种相对奇特的激光器,其中光放大是在波动器中实现的,由来自电子加速器的高能(相对论)电子馈送。 这种设备已经证明,发射波长从太赫兹区域通过中红外和近红外,可见光和紫外线范围到达X射线区域,即使没有单个设备可以跨越整个波长范围。
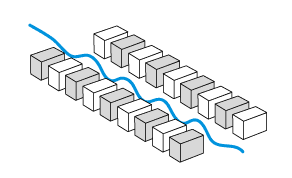
图1:设置波动器,如自由电子激光器中使用的。周期性变化的磁场迫使电子束(蓝色)在略微振荡的路径上,从而导致辐射的发射。
在波动器中,磁铁(永磁体或电磁铁)的周期性排列产生周期性变化的洛伦兹力,迫使电子以取决于电子能量、波动器周期和(弱)磁场强度的频率辐射。 自发发射和受激发射都会发生,允许在特定波长范围内进行光放大。
自由电子激光器最大的吸引力是:
- 它们能够在非常宽的波长区域工作
- 单个设备可实现大波长调谐范围
- 在极端波长区域具有出色的性能,这是任何其他光源都无法达到的
与其他同步辐射源(纯波动器和摆动器)相比,FEL可以产生具有更高光谱亮度和相干性的输出。 这对于许多应用非常有用,包括原子和分子物理学、超快 X 射线科学、高级材料研究、超快化学动力学、生物学和医学等领域。
FEL的最大缺点是它们的设置非常大且昂贵,因此它们只能在世界上相对较少的大型设施中使用。 在汉堡进行了一项雄心勃勃的自由电子激光项目(欧洲XFEL,最初在TESLA项目中,现在在欧洲项目中)[17]。 3.4公里长的XFEL可产生具有前所未有的性能特征的硬X射线输出:波长低至0.05 nm,脉冲持续时间低于100 fs,以及极高的亮度。 SLAC的LCLS已经实现了低于0.15 nm的激光波长,对应于10 keV的光子能量。
参考文献
[1] L. R. Elias et al., “Observation of stimulated emission of radiation by relatistic electrons in a spatially periodica transverse magnetic field, Phys. Rev. Lett. 36, 717 (1976), doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.36.717
[2] D. A. G. Deacon et al., “First operation of a free-electron laser”, Phys. Rev. Lett. 38 (16), 892 (1977), doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.38.892
[3] A. M. Kondratenk and E. L. Saldin, “Generating of coherent radiation by a relativistic electron beam in an ondulator”, Part. Accel. 10, 207 (1980)
[4] C. A. Brau, “Free-electron lasers”, Science 239 (4844), 1115 (1988), doi:10.1126/science.239.4844.1115
[5] K.-J. Kim and A. Sessler, “Free-electron lasers: present status and future prospects”, Science 250, 88 (1990), doi:10.1126/science.250.4977.88
[6] G. R. Neil and L. Merminga, “Technical approaches for high-average-power free-electron lasers”, Rev. Mod. Phys. 74, 685 (2002), doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.74.685
[7] W. Ackermann et al., “Operation of a free-electron laser from the extreme ultraviolet to the water window”, Nature Photon. 1, 336 (2007), doi:10.1038/nphoton.2007.76
[8] P. Emma et al., “First lasing and operation of an ångstrom-wavelength free-electron laser”, Nature Photon. 4, 641 (2010), doi:10.1038/nphoton.2010.176
[9] W. A. Barletta et al., “Free electron lasers: Present status and future challenges”, Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 618, 69 (2010), doi:10.1016/j.nima.2010.02.274
[10] J. N. Galayda et al., “X-ray free-electron lasers – present and future capabilities”, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 27 (11), B106 (2010), doi:10.1364/JOSAB.27.00B106
[11] E. C. Snively et al., “Broadband THz amplification and superradiant spontaneous emission in a guided FEL”, Opt. Express 27 (15), 20221 (2019), doi:10.1364/OE.27.020221
[12] N. S. Mirian et al., “Generation and measurement of intense few-femtosecond superradiant extreme-ultraviolet free-electron laser pulses”, Nature Photonics 15, 523 (2021), doi:10.1038/s41566-021-00815-w
[13] E. Prat et al, “A compact and cost-effective hard X-ray free-electron laser driven by a high-brightness and low-energy electron beam”, Nature Photonics 14, 748 (2020), doi:10.1038/s41566-020-00712-8
[14] W. Decking et al., “A MHz-repetition-rate hard X-ray free-electron laser driven by a superconducting linear accelerator”, Nature Photonics 14, 391 (2020), doi:10.1038/s41566-020-0607-z
[15] The World Wide Web Library on Free Electron Lasers, http://sbfel3.ucsb.edu/www/vl_fel.html
[16] The LCLS (Linac Coherent Light Source) at SLAC (Stanford), https://lcls.slac.stanford.edu/
[17] The European X-ray laser project XFEL, https://www.xfel.eu/



