定义
一种依靠自聚焦测量材料Kerr非线性强度的技术。
Z 扫描测量技术[1,2]通常用于测量Kerr非线性的强度(即非线性指数的大小 n2) 的光学材料。从本质上讲,被研究材料的样品通过激光束的焦点移动,并且光束半径(或轴上强度)作为样品位置的函数在焦点后面的某个点进行测量。这些量受自聚焦效应的影响。如果非线性指数为正,并且样品位于焦点后面(如图1所示),则自聚焦会减少光束发散,从而增加检测器信号。如果将样品移动到焦点的左侧,则焦点将向左移动,焦点后较强的散度会降低检测器信号。根据检测器信号对样品位置的测量依赖性,可以计算出非线性指数的大小。
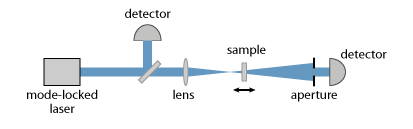
图 1:设置 z 扫描测量。通过孔径的透射率是作为样品位置的函数来测量的。左侧探测器用于监测入射脉冲能量。
请注意,非线性吸收,例如双光子吸收,也会影响测量信号。然而,这可以通过记录整个发射光束的功率来单独测量。有了这些数据,非线性的测量就可以得到纠正。
参考文献
[1] M. Sheik-Bahae et al., “High-sensitivity, single-beam n2 measurements”, Opt. Lett. 14 (17), 955 (1989), doi:10.1364/OL.14.000955
[2] M. Sheik-Bahae et al., “Sensitive measurement of optical nonlinearities using a single beam”, IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 26 (4), 760 (1990), doi:10.1109/3.53394
[3] J. Wang et al., “Time-resolved Z-scan measurements of optical nonlinearities”, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 11 (6), 1009 (1994), doi:10.1364/JOSAB.11.001009
[4] S. Hughes et al., “Fast Fourier transform techniques for efficient simulation of Z-scan measurements”, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 12 (10), 1888 (1995), doi:10.1364/JOSAB.12.001888
[5] S. M. Mian et al., “Effects of beam ellipticity on Z-scan measurements”, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 13 (5), 856 (1996), doi:10.1364/JOSAB.13.000856
[6] R. de Nalda et al., “Limits to the determination of the nonlinear refractive index by the Z-scan method”, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 19 (2), 289 (2002), doi:10.1364/JOSAB.19.000289
[7] I. P. Nikolakakos et al., “Broadband characterization of the nonlinear optical properties of common reference materials”, IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 10 85), 1164 (2004), doi:10.1109/JSTQE.2004.836007
[8] B. Gu et al., “Theory of Gaussian beam Z scan with simultaneous third- and fifth-order nonlinear refraction based on a Gaussian decomposition method”, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 22 (12), 2651 (2005), doi:10.1364/JOSAB.22.002651
[9] M. C. Fischer et al., “Simultaneous self-phase modulation and two-photon absorption measurement by a spectral homodyne Z-scan method”, Opt. Express 16 (6), 4192 (2008), doi:10.1364/OE.16.004192
[10] L. C. Oliveira and S. C. Zilio, “Single-beam time-resolved z-scan measurements of slow absorbers”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 65, 2121 (1994)
[11] T. Olivier et al., “Nanosecond Z-scan measurements of the nonlinear refractive index of fused silica”, Opt. Express 12 (7), 1377 (2004), doi:10.1364/OPEX.12.001377
[12] L. Pálfalvi et al., “A general Z-scan theory”, Appl. Phys. B 97 (3), 679 (2009)



